Endocrine System: Chemical Communication

The endocrine system refers to a collection of glands that secrete hormones into the circulatory system to target a distant organ with chemical messages. These tend to be slower processes, such as growth, menstrual cycles, or circadian rhythms, but also refer to procedures for dealing with stress and the environment. The notable endocrine glands are:
- the pituitary gland – about the size of a pea, this gland protrudes at
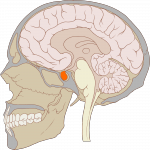 the base of the hypothalamus, there are two lobes in humans that regulate growth, blood pressure, pregnancy and childbirth, breast milk production, sex organ functioning, thyroid gland function, metabolism, osmolarity and water balance, temperature regulation, pain relief and sleeping patterns (but this is mostly the responsibility of the pineal gland. This is the seat of control of the mind over the entire body, hormonally speaking.
the base of the hypothalamus, there are two lobes in humans that regulate growth, blood pressure, pregnancy and childbirth, breast milk production, sex organ functioning, thyroid gland function, metabolism, osmolarity and water balance, temperature regulation, pain relief and sleeping patterns (but this is mostly the responsibility of the pineal gland. This is the seat of control of the mind over the entire body, hormonally speaking. - the pineal gland – The gland produces melatonin to regulate sleep cycles and circadian rhythm and the hormone is very sensitive to light. Descartes viewed the gland as the gateway between the body, mind, and soul and considered it to be the third eye. When children become teenagers, production becomes delayed leading to later sleeping and waking times.
- the pancreas – largely regulates the digestive and lymphatic
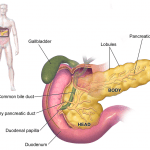 systems, secreting insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, pancreatic peptide, and assists in digestion by secreting pancreatic which is a blend of digestive enzymes
systems, secreting insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, pancreatic peptide, and assists in digestion by secreting pancreatic which is a blend of digestive enzymes - ovaries, testes – ovaries release: estrogen, testosterone, progesterone, and unfertilized eggs; testicles release sperm and androgen (steroid hormones, primarily testosterone)
- thyroid gland – one of the largest endocrine glands with two lobes around the trachea, below the thyroid cartilage also known as the Adam’s apple. It controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and uses other hormones. It does this by producing hormones that regulate growth and rate of function of othe
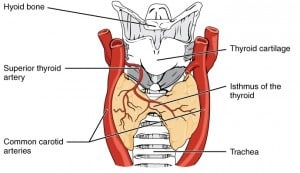 r systems. Hormonal output of the thyroid gland is controlled by thyroid stimulating hormone produced by the anterior pituitary lobe, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone produced by the hypothalamus
r systems. Hormonal output of the thyroid gland is controlled by thyroid stimulating hormone produced by the anterior pituitary lobe, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone produced by the hypothalamus - parathyroid gland – Humans usually have four, located on the back of the thyroid gland that produce parathyroid hormone and calcitonin. Together, these hormones regulate bone physiology including calcium levels and phosphate levels and reabsorption levels via the kidneys, so that the levels of these chemicals are optimal for the nervous and muscular systems to function
- hypothalamus – a small portion of the brain located just above the brain stem with specialized cells to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. All vertebrate brains have a hypothalamus, which produce neurohormones that stimulate the secretion of pituitary hormones, controlling body temperature, hunger, thirst, and fatigue, different processes of the autonomic nervous system.
- gastrointestinal tract – releases hormones to help regulate the digestive process, including gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin, and ghrelin
- adrenal glands – endocrine glands that sit atop the kidneys, responsible for stress hormones cortisol and corticosteroids, and also catacholamines, like adrenaline and noradrenaline. These cells also produce androgens to assist the body in dealing with stress, and the glands activate both the nervous and endocrine systems to work react to stress.
These glandular organs together make up the endocrine system, which sends chemical messages throughout the body, similar to the nervous system, however, the effects and mechanisms of the system are very different in their processes.
Glands? What are those?
The word gland is used for any organ that is used to excrete hormones for release into the bloodstream or into cavities inside of the body or to its outer surface. There are also two types of glands to be aware of: endocrine and exocrine; the latter uses ducts and bodily cavities for transport while the former uses the circulatory system for transport.
The exocrine system is a collection of glands that operates differently than the endocrine system, but is extremely useful to the body. The exocrine system uses three different methods of excretion:
- Merocrine glands – cells excrete their substances by exocytosis (cellular waste removal by containing the waste,then releasing it
outside of the cell): i.e. pancreatic acinar cells
It is easiest to understand the exocrine system by how it functions: it comprises sweat glands, salivary glands, mammary glands, and the liver. Together, the exocrine and endocrine systems work all of the glands of the body to remove waste.
Endocrine System Bodily Operations
The endocrine system operates differently from the exocrine system, in that it works via the circulatory system. Many organs have secondary endocrine functions in addition to their primary roles in the body. Endocrine organs usually signal themselves in groups and in certain orders, referred to as an axis. The Greek words ἐνδο- endo-, inside or interior and κρίνειν krinein, to separate or distinguish are useful for understanding what the endocrine system does. It is essentially specializing specific organs to work in unison for specific bodily functions, including growing, sleeping, and the most basic of physiological needs, such as hunger and urination. In unison with the nervous system, this is how the body communicates internally.
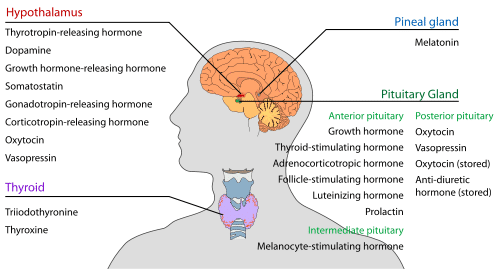
I will go into more detail in later articles about the particular neuroreceptors and hormones that the body uses for specific functions. Keep in mind that many are still unclassified and have properties that have not yet been observed and measured. The science of endocrinology and neurology have vast horizons to cover before we truly understand how these systems interrelate and function to produce conscious thought. But here are some great graphics of the known hormones and their organs of origin, thanks wikipedia!

1 thought on “Endocrine System – The Body’s Way of Talking”