Femur Bone Anatomy: Pillars of Support for the Human Skeleton
Introducing the most Massive and Strong (in most ways) Bone in the Human Body
There are 62 bones in the legs: 10 trunk/hip bones, 14 ankle bones, and 38 foot bones. The femur (thigh) is the largest and strongest of these bones. Most land mammals capable of jumping also have femur bones, also lizards, frogs, and other tetrapod vertebrates. Its length on average is 26.74% of a person’s height, a ratio found in both men and women and most ethnicities with only restricted variation.

5 Interesting Femur Bone Statistics
- The femur is, on average, about 1/4 of a person’s height. It’s remarkably strong and can withstand forces of up to 1,800 to 2,500 pounds (800 to 1,100 kilograms) of pressure, making it one of the strongest bones in the body.
- The Femoral neck sits at a 125 degree angle
- Vehicular accidents are the primary cause of breakage
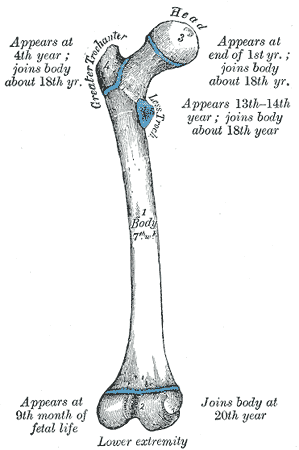
- During growth in childhood and adolescence, the proximal end of the femur (the femoral head) has a growth plate, known as the epiphyseal plate. This growth plate allows for longitudinal growth and helps determine a person’s final height when it closes.
- Forensic anthropologists often use the femur bone to estimate the age of an individual based on the degree of fusion of the epiphyseal plates, which can help in identifying human remains. It is heavily used in archaeology.
The Greater Trochanter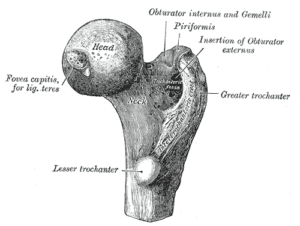
The Great Trochanter is a large, irregular, quadrilateral eminence on the upper portion of the femur bone. This portion of the bone has several, extremely important muscle insertions for the thigh and hip bones:
The lateral surface, quadrilateral in form, is broad, rough, convex, and marked by a diagonal impression, which extends from the postero-superior to the antero-inferior angle, and serves for the insertion of the tendon of the gluteus medius.
Above the impression is a triangular surface, sometimes rough for part of the tendon of the same muscle, sometimes smooth for the interposition of a bursa between the tendon and the bone. Below and behind the diagonal impression is a smooth triangular surface, over which the tendon of the gluteus maximus lies, a bursa being interposed.
The medial surface, of much less extent than the lateral, presents at its base a deep depression, the trochanteric fossa (digital fossa), for the insertion of the tendon of the obturator externus, and above and in front of this an impression for the insertion of the obturator internus and superior and inferior gemellus muscles.
Reference: (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Greater_trochanter)
The Lesser Trochanter
The Lesser trochanter is on the underside of the femoral head and also has several muscular insertions: The Psoas Major on bottom and the Illiacus on top.
The Femoral Head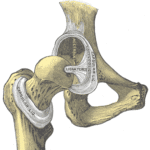
The Femoral Head is the highest part of the femur bone, support by the femoral neck. It inserts as a ball/socket joint into the Hip/Ilium via the structure depicted to the right.
The Femoral Neck
The Femoral neck usually sits at a 120-135 degree angle with some variation. A fracture of this area is known as a hip fracture and happens during aging. This structure supports the head of the femur bone and its insertion into the hip.
 The Femoral Body
The Femoral Body
The Shaft of the femur is somewhat curved and has a protruding ridge called the linea aspera (rough line). The area of the bone supports the strongest muscle tissue in the body, including the hamstrings, Quadriceps, and thigh musculature. The Vastus Laterallis (outer quadricep) and adductor magnus (inner thigh muscle) connects into the linea aspera.
Lower Portion of the Femur
How the Femur Bone affects your Holistic Health
Femur bone fractures correlate with increased disease in the elderly. It is safe to say that the femur bone is an organ that houses much of the mineral deposits for the body. Therefore, as we age and the bone tissue become more porous, this bone become one of the primary areas of decomposition.
Bone Marrow and the formations of new blood cells
Red Bone Marrow
- Red bone marrow is the primary site for hematopoiesis, the formation of blood cells.
- It is located in the cavities of certain bones, including the femur, pelvis, ribs, vertebrae, and sternum.
- Red marrow consists of a network of blood vessels, various types of blood-forming cells, and supporting tissue called stroma.
- Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) within the red marrow are the source of all blood cells. These stem cells have the remarkable ability to differentiate into various types of blood cells.
- Red marrow is highly active in producing blood cells during early life when there is a significant need for rapid growth and the formation of a robust blood cell population.
- Red marrow plays a vital role in supporting the high demand for red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets in growing children.
- Red marrow primarily produces red blood cells, white blood cells (granulocytes, lymphocytes, and monocytes), and platelets.
- Red blood cells are responsible for oxygen transport in the body.
- White blood cells play a vital role in the immune system’s defense against infections.
- Platelets are essential for blood clotting and wound healing.
Bone Marrow during the aging process:
- As an individual grows and matures, some of the red bone marrow within the femur and other long bones gradually undergoes a transformation into yellow bone marrow.
- This transformation involves the conversion of hematopoietic (blood-forming) tissue into adipose (fat) tissue.
- The shift from red to yellow marrow is part of a natural process that occurs with aging and is influenced by factors such as hormonal changes and the body’s decreasing need for rapid blood cell production.
- While yellow marrow is predominant in the central cavity of long bones like the femur in adults, red marrow still exists in other locations, such as the axial skeleton (e.g., pelvis, sternum, vertebrae).
- Red marrow retains its hematopoietic activity in these areas and can be mobilized when there is a greater demand for blood cell production, such as in response to illness, injury, or certain medical conditions.
Yellow Bone Marrow
- Yellow bone marrow is found in the central cavities of long bones, including the shaft of the femur.
- It contains fewer blood-forming cells and is mainly composed of fat cells (adipocytes).
- Yellow marrow stores fat and serves as an energy reserve for the body.
- In certain circumstances, such as severe blood loss or chronic anemia, yellow marrow can transform back into red marrow to help replenish blood cell populations.
Adaptive Response of the Femur Bone:
- The femur bone, like other bones in the body, can adapt to changing physiological needs.
- In cases of severe blood loss, chronic anemia, or other conditions that require increased blood cell production, the femur’s red marrow can become more active, and additional sites within the femur may transition from yellow to red marrow to support hematopoiesis.
One of the primary aspects of bone health is acquiring enough calcium to maintain bone density. Most calcium is available via leafy green vegetables, notably kale, bok-choy, and broccoli. Sodas and carbonated beverages make it harder for the body to absorb calcium and should be avoided by those with osteoporosis (orthoinfo.com). Vitamin D is an important catalyst for absorbing calcium into the bloodstream.
Phosphorus is another vital nutrient to maintain bone health. Nuts, Sesame Seeds, peanut butter, parsley, crab and prawns are all foods high in phosphorus. Don’t feel like you have to eat meat or drink milk to get these essential nutrients.
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Femur_neck
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Greater_trochanter
- https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/staying-healthy/calcium-nutrition-and-bone-health
Femur Bone Anatomy: Pillars of Support for the Human Skeleton Read More »