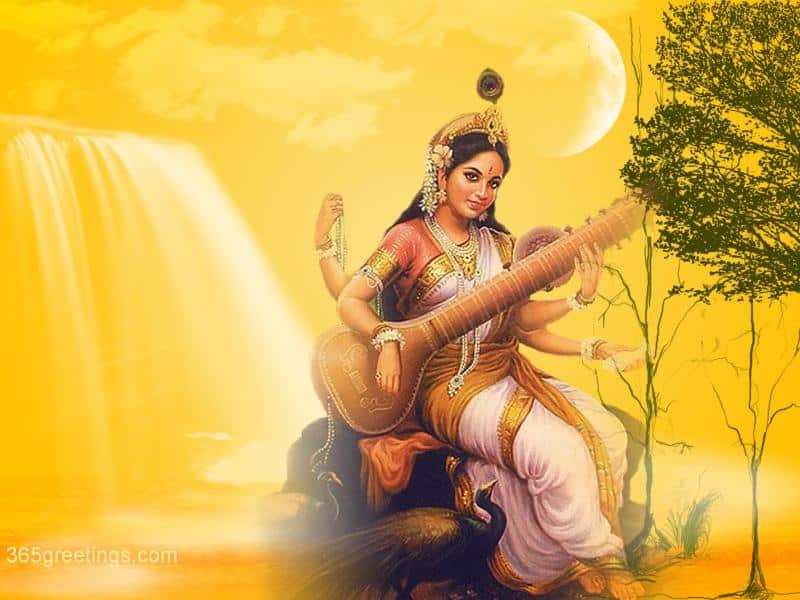
Saraswati | Sarasvatī | सरस्वती
Saraswathi is a Hindu goddess, part of the trinity with Lakshmi and Parvati; she is a representation of knowledge, music, arts, wisdom, and learning. The three forms of the female goddess assist Vishnu, Shiva, and Brahman their partners while they sustain the universe . The goddess is revered by Jains and Buddhists as well as Hindus. … Read more