Mula Bandha | मूल बंध (Bandhas part 1/4)
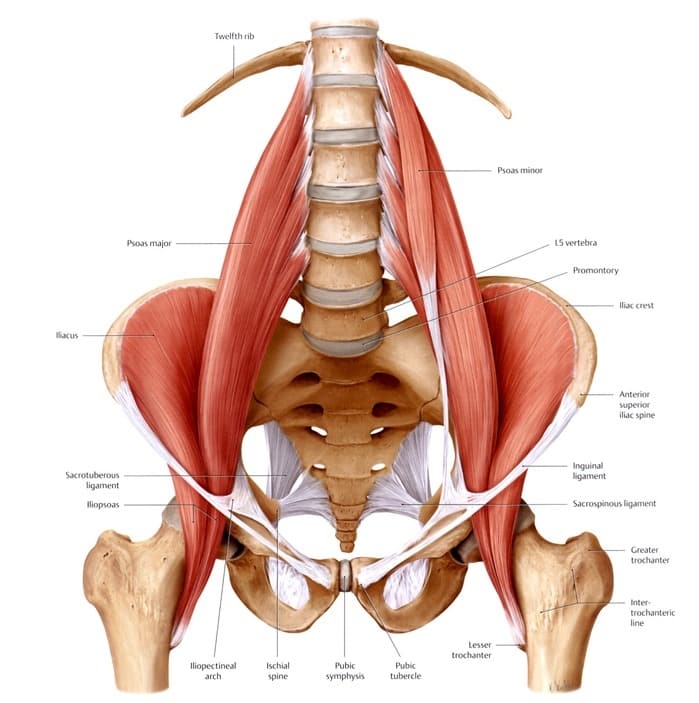
The Mula Bandha and the Perineal Muscles Sanskrit for “MULA” – मूल In Sanskrit, Mula means “root”, foundation, origin, source, and beginning. Bandha means energy lock, bond, hold, or harness. Mula bandha is the root of the body, the excretion point and the bottom of the spine. This is the same as the perineal muscle group … Read more