A Yogi’s Guide to Prana, Vitality, and Life-Force
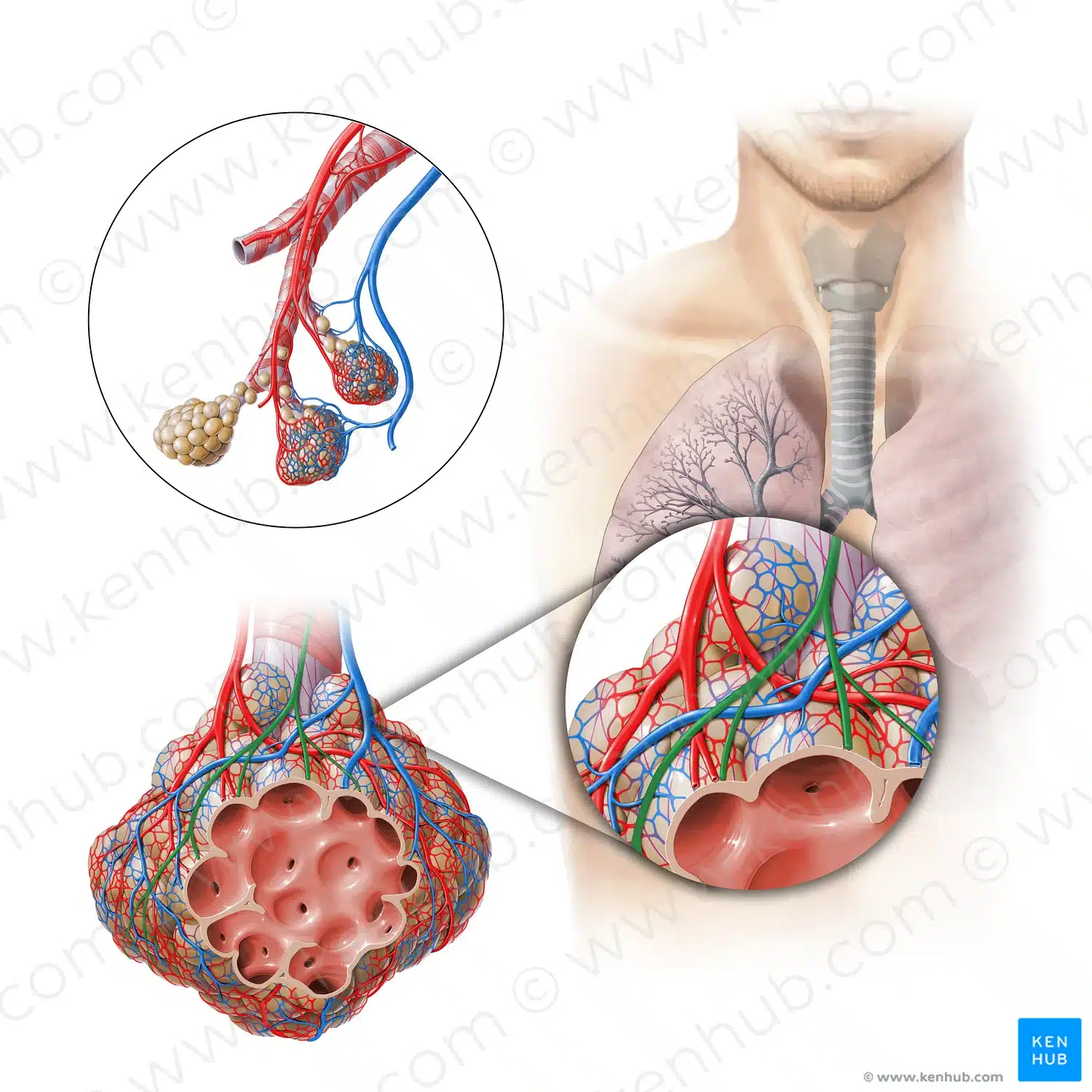
To sustain life, a body must produce sufficient energy through aspiration. Breathing is perhaps the only system of the body that is both autonomic and conscious depending completely on the awareness and focus of the breather.
Breathing through the nose, all the time, is part of the true yogi’s path. I can remember 6 months into practicing yoga, I attained the ability to breathe through my nose and it complete changed my yoga practice and my life. I got hooked on the feeling of yoga (call it a healthy addiction) and never looked back.
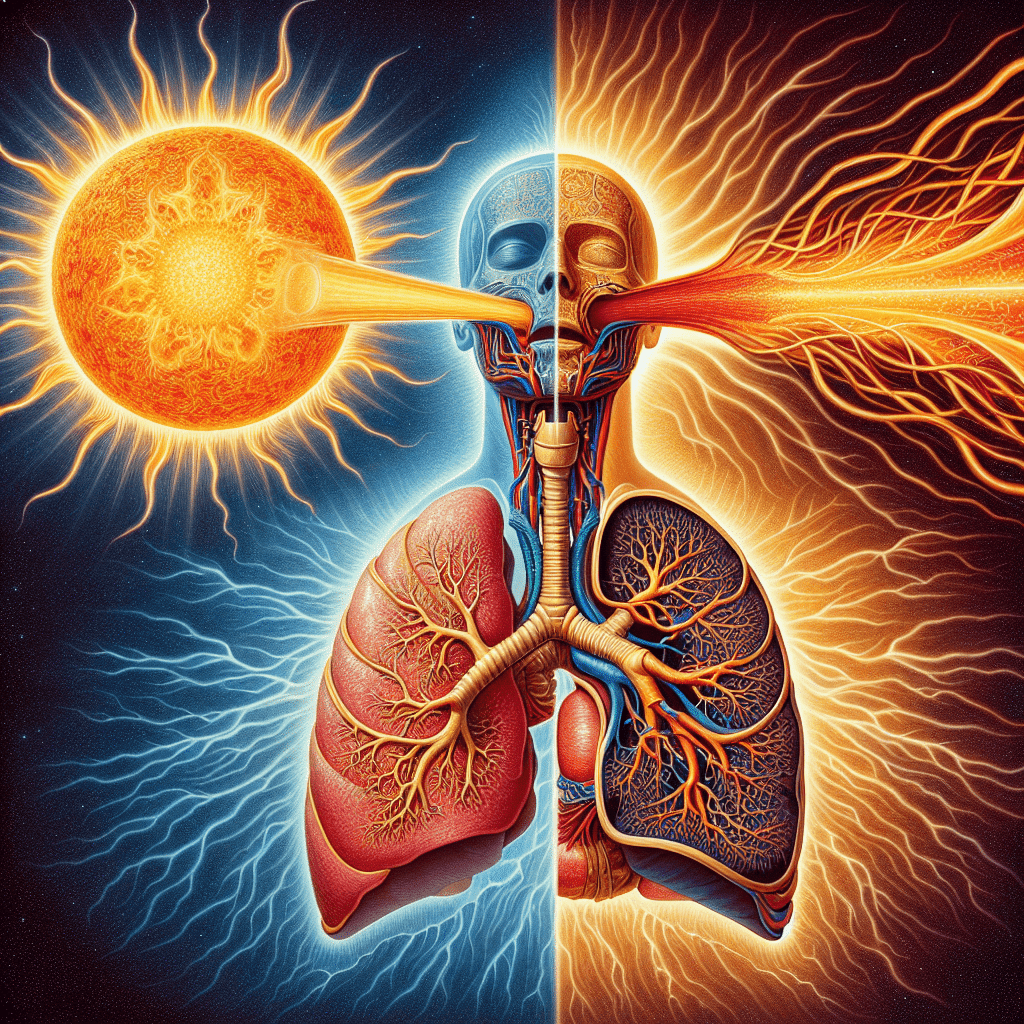
In Yoga, the energy of breath is called prana (प्राण, prāṇa) which can be described as solar wind in the atmosphere, or liquid light[6]. Through ventilated aspiration, the yogi ingests the prana into the nervous system. In Hindu literature, Prana is described as originating from the Sun and connecting the elements through the Chakras of the human nervous system and conscious awareness.
The nervous system is completely dependent on your breathing to function: The parasympathetic system slows your breathing rate. It causes your bronchial tubes to narrow and the pulmonary blood vessels to widen. The sympathetic system increases your breathing rate. It makes your bronchial tubes widen and the pulmonary blood vessels narrow.[4] This process of is also known as the “fight or flight” response. This happens through ventilation, or respiration as the body mobilizes itself to a threat. However, this system is over-active in our cultures because of our stress responses to non-life threatening stimuli. It is healthier for a human to regularly breathe through the nose.
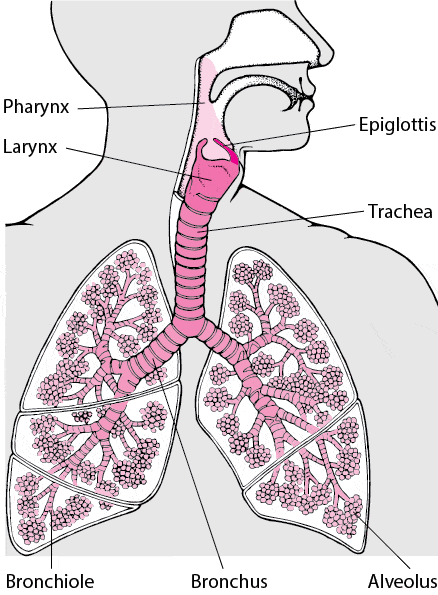
The Nasal Cavity
“The function of the nasal cavity is to warm, moisturize, and filter air entering the body before it reaches the lungs.[1]” Here are the additional benefits:
Nose breathing is beneficial primarily because it allows your nasal cavities to:[2]
- reduce exposure to foreign substances.
- humidify and warm inhaled air.
- increase air flow to arteries, veins, and nerves.
- increase oxygen uptake and circulation.
- slow down heart rate.[3]
- improve lung volume.
- help your diaphragm work properly.
In essence, hairs and mucus lining the nasal cavity help to trap dust, mold, pollen and other environmental contaminants before they can reach the inner portions of the body and the lung’s organic tissue. Air exiting the body through the nose returns moisture and heat to the nasal cavity before being exhaled into the environment.[1] The mouth, also known as the oral cavity, is the secondary external opening for the respiratory tract. The mouth is mostly for filtering in eating and drinking.
Focus on the Exhale
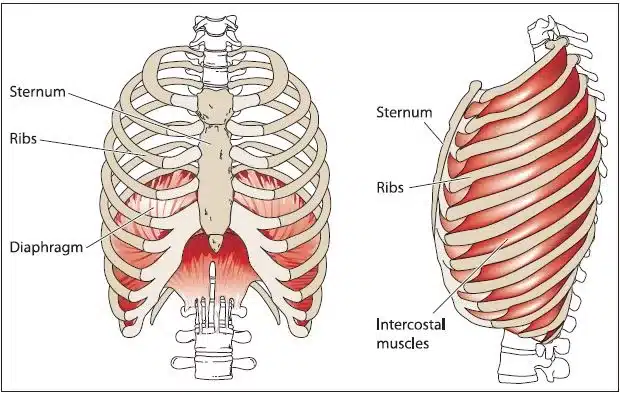
Nasal exhalations are an extremely important focus in yoga. The muscles in your chest and abdomen tighten or contract to create a slight vacuum around the lungs. This causes air to flow in. When you exhale, the muscles relax and the lungs deflate on their own, much like an elastic balloon will deflate if left open to the air. The lungs are extremely flexible sacks of tissue that have the ability to expand and contract.
References: