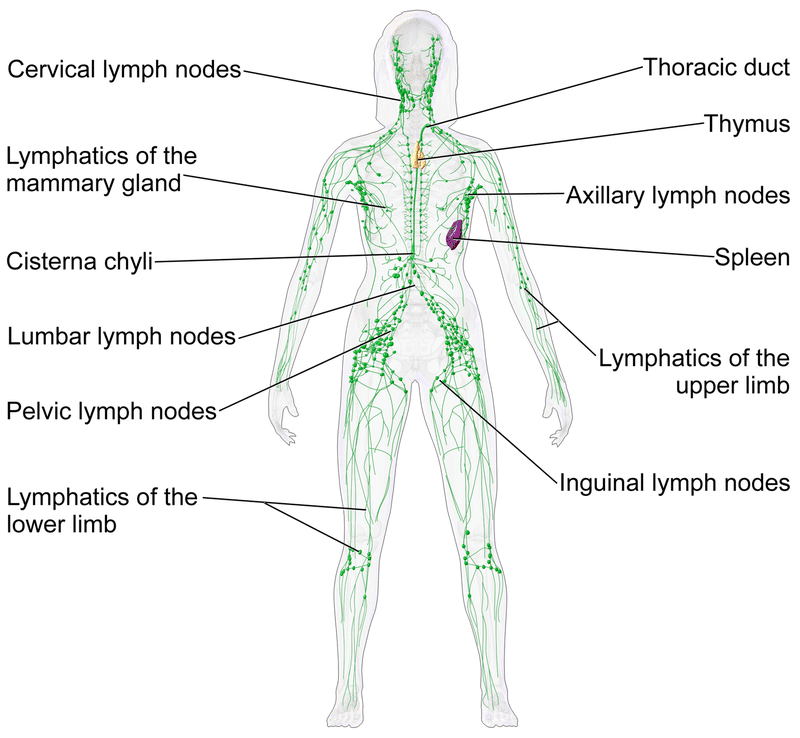
The Lymphatic system works in conjunction with the circulatory system to reroute 3 liters of the ~20 processed each day by the body to replace plasma in the blood. Lympha is the Latin word for ‘water’ and refers to the clear liquid that provides autoimmune defense and assists with digestion. The Lymphatic system works alongside the circulatory system to remove waste, toxin, and provide defense for the body from pathogens, infection, and disease.
In order to continue, we have to examine a few of the different fluids in the body:
- Blood Plasma – the pale yellow liquid in blood, makes up 55% of the bodies total blood, is made up of 95% water, and contains
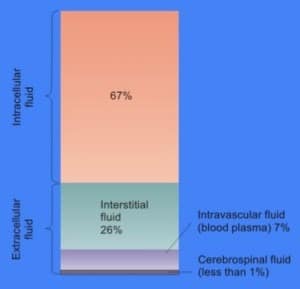 dissolved proteins, glucose, coagulation factors, electrolytes, hormones, and carbon dioxide
dissolved proteins, glucose, coagulation factors, electrolytes, hormones, and carbon dioxide - Intracellular Fluid – Cytosol, or intracellular fluid, is the liquid found inside of cells separated into compartmental membranes
- Extracellular Fluid – fluid outside of cells, mainly blood plasma and interstitial fluid that, in conjunction with intracellular fluid, helps to control movement of electrolytes and water in the body
- Interstitial Fluid – surrounds the cells of multicellular animals, and is found between the tissue spaces, is very similar to plasma, and pushes water out of capillaries to dispose of waste and continuously reinvigorate the blood stream with water using osmosis and hydrostatic pressure.
- Transcellular Fluid – the total body water contained within epithelial lined spaces (gastrointestinal, cerebrospinal, peritoneal, and ocular fluids)
We also have to examine the two different parts of the immune system:
- the innate immune system – provides immediate defense against infection, found in all plant and animal life. Evolutionarily, this is a much older defense system and is dominant in plants, fungi, insects, and very primitive multicellular organisms. This system activates the adaptive immune system in multicellular organisms
- the adaptive immune system – also known as acquired immunity, this is a subsystem composed of highly specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate and/or prevent pathogen growth. This creates immunological memory in response to specific pathogens leading to enhanced responses with subsequent encounters. This is the entire basis of vaccination. Pathogen specific receptors are acquired during the lifetime of the organism. This can be helpful in cases where the body adapts positively, or this can be harmful when autoimmune diseases are acquired. This system is highly adaptable because of somatic hypermutation and somatic recombination (V(D)J recovery) allows for agile re-creation of anti-body cells to fight new pathogens. The antigen receptors are then uniquely expresses on each lymphocyte. This brings us back to where we started….
The Lymph system is therefore extremely involved in the body’s response to pathogens, viruses, and bacteria. Both the innate and adaptive immune systems have humoral and cell mediated immunities (humoral refers to lymph fluid). Remember the two systems, and how blood is contained in a closed system, and lymph is more open. This is a major part of what takes waste out of the bloodstream, and more specifically, how the body fights off infection and eliminates harmful micro-organisms.
So all together, your body is consistently reproducing certain cells to fight off bad guys. and it uses this liquid transport system, which is open around the blood vessels, to do it. This is the final piece of the puzzle, the different types of adaptive immune cells called lymphocytes:
- Killer T cells – a subgroup of T cells that kills cells infected with a virus or that are damaged or dysfunctional
- Helper T cells – regulate both innate and adaptive immune responses to help determine the body’s response
- Gamma Delta T cells – these cells are hard to classify and skirt the border between innate and adaptive cells.
- B lymphocytes and antibodies – identifies pathogens then (this is where the magic happens, this is from Wikipedia) this antigen/antibody complex is taken up by the B cell and processed by proteolysis into peptides. The B cell then displays these antigenic peptides on its surface MHC class II molecules. This combination of MHC and antigen attracts a matching helper T cell, which releases lymphokines and activates the B cell.[61] As the activated B cell then begins to divide, its offspring (plasma cells) secrete millions of copies of the antibody that recognizes this antigen. These antibodies circulate in blood plasma and lymph, bind to pathogens expressing the antigen and mark them for destruction by complement activation or for uptake and destruction by phagocytes. Antibodies can also neutralize challenges directly, by binding to bacterial toxins or by interfering with the receptors that viruses and bacteria use to infect cells.[62]
So essentially, these specialized cells identity, swarm, and kill pathogens, using the lymph system for circulation and of powerful anti-pathogen cells. This is why the body’s fluid content is so important; it allows the body to regulate and defend itself.
Now let’s talk a bit about the specific organs of the lymphatic system:
- Lymph vessels – these conduct lymph between the different parts of the body. The lymph vessels transport lymph back to the blood stream replacing the volume lost from the blood during the formation of the interstitial fluid
- Thymus – The Thymus is extremely important for the immune system, it is where T cells mature, in front of the heart and behind the sternum. It has two lobes that surround the trachea
- Spleen – an organ found in all vertebrates, this is similar to a very large lymph node to act primarily as a blood filter. It is possible to remove the spleen and maintain life. It recycles iron and stores blood; it also synthesizes antibodies. Its absence will cause predisposition to certain infections.
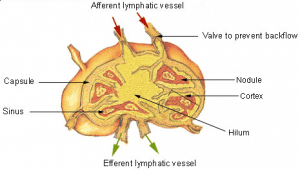
- lymph nodes – an organized collection of lymph tissue that lymph fluid passes through on its way back to the blood stream.
- lymph follicle – A lymph follicle is a dense collection of lymphocytes, the number, size and configuration of which change in accordance with the functional state of the lymph node
So you can see that the system works very much in unison with the other bodily systems, mainly the circulatory and gastrointestinal systems to remove wasteful byproducts and toxins involved in consuming food orally. You can feel the concentrations of lymph nodes on the sides of your neck, at the top of the rib cage, and on the soft portion of the elbows and knees.
I think I will post another article on the adaptive immune system, there is just so much here. This should be pretty comprehensive on the lymph system as a whole, but ask any questions and I’ll try to figure it out!