What Does Cold Weather do to Your Body?
Cold Weather and Lower Temperatures Affect the Human Body The Human Body is made to deal with the Cold Cold Temperatures stress the body, but the human body is meant to adapt to colder conditions. You see, low temperatures stress the body; but in a way, it is a very psychological phenomenon. It happens in … Read more




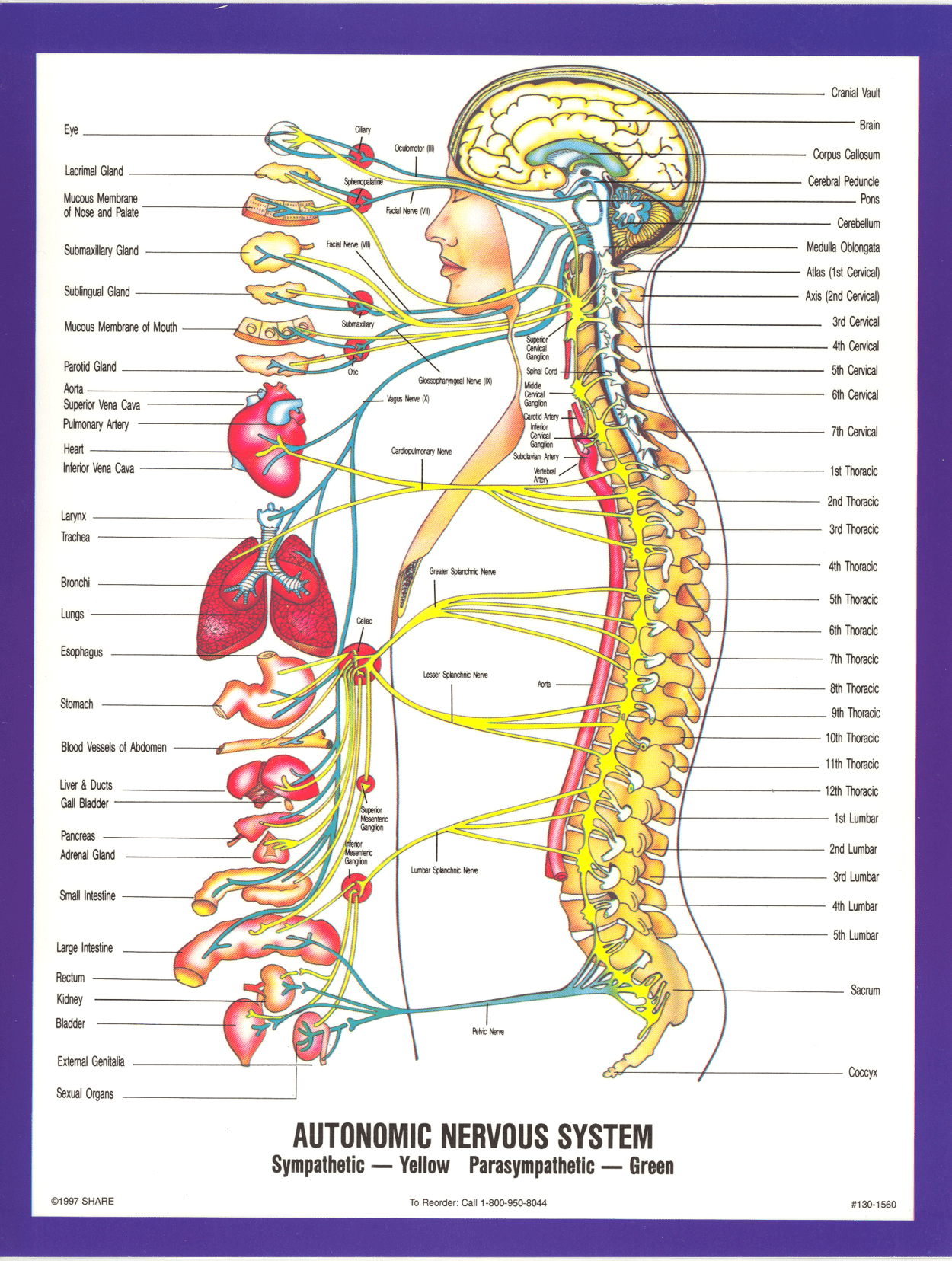

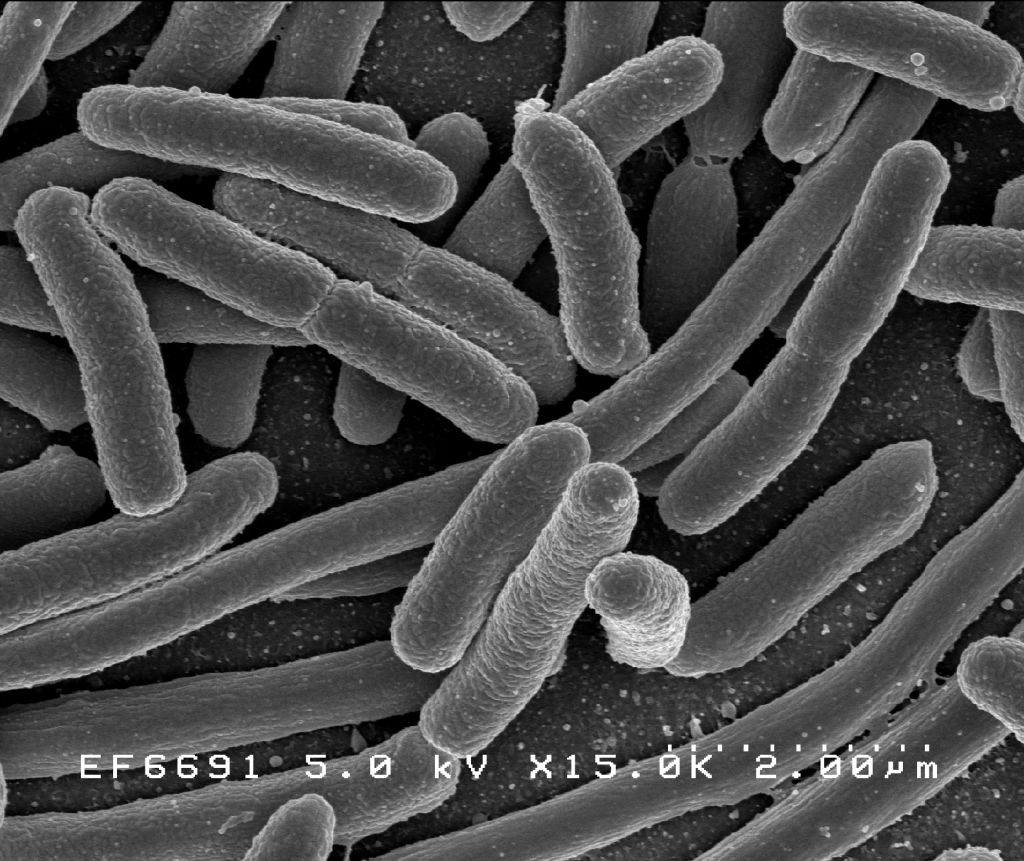
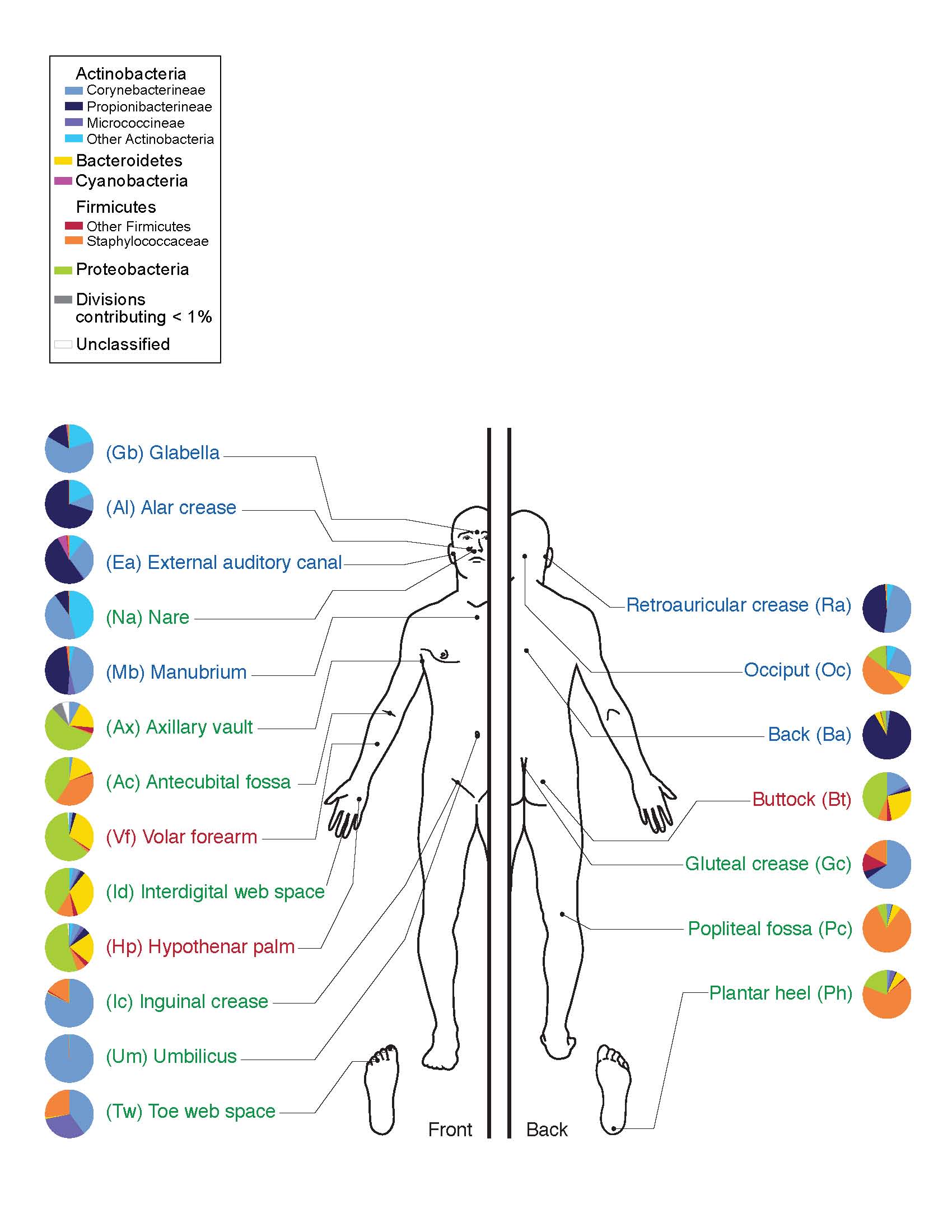
![By Photo Credit: Janice Carr Content Providers(s): CDC/ Segrid McAllister [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons](https://elliottelford.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/epidermis_microbiota.png)