Endocrine System – The Body’s Way of Talking
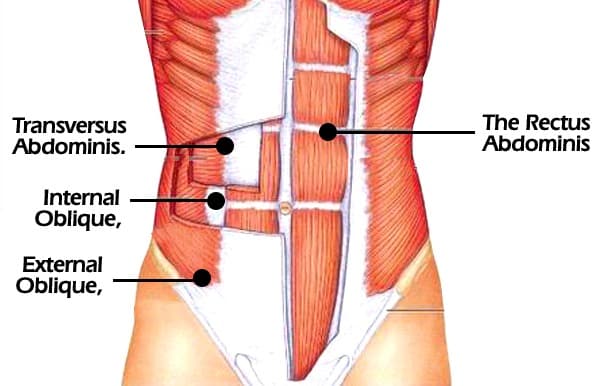
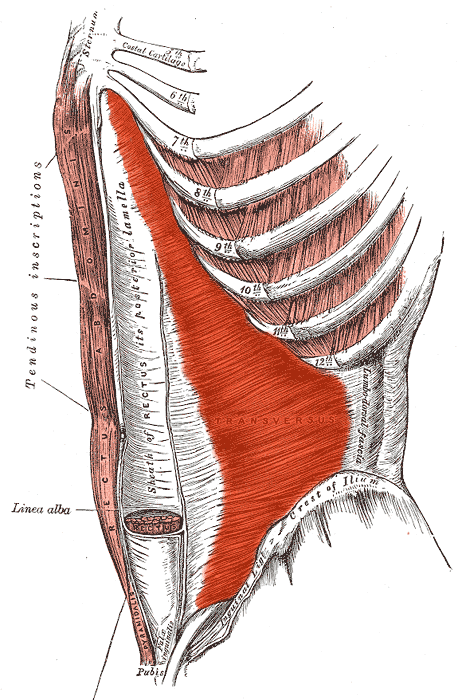
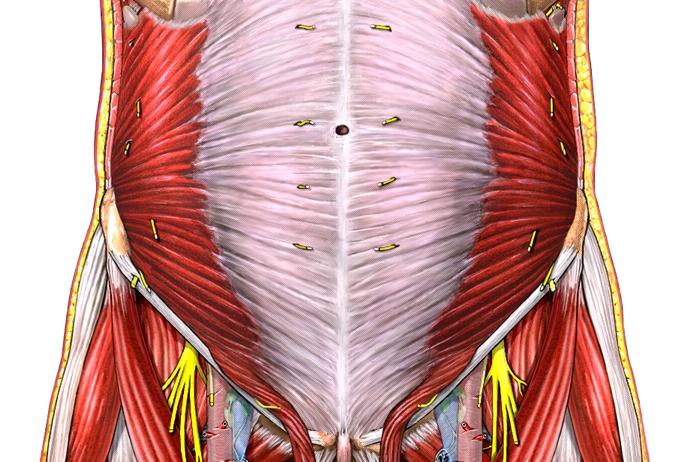
The endocrine system refers to a collection of glands that secrete hormones into the circulatory system to target a distant organ with chemical messages. These tend to be slower processes, such as growth, menstrual cycles, or circadian rhythms, but also refer to procedures for dealing with stress and the environment.