Nose Breathing & the Lungs
The Benefits of Nasal Breathing
Ventilation and The Sympathetic Nervous System

Breathing is a fundamental act of life. In humans, breath represents the gateway between the mind and the body. Also called ventilation, it is the first action we take when we are born, and the last before we die. The lungs are the primary mover of energy within the body; when stressed, the breathing rate elevates. Yogis and practitioners of meditation are particularly interested in breathing as a way of becoming more aware of the body.
Ideally, a yogi can breath in and out through their nostrils ceaselessly. Some people have physical limitations in their ability to do this, so as always, consideration must be taken the unique deviations of an individual skeleton. The physiological difference between breathing through your nose and through your mouth is tremendous. Clearing your nasal and air passageways can be a simple part of daily maintenance, or caring for the body’s optimal organic function. Yoga is the exercise of “stilling the mind” through the restricted the flow of breath. Using the nostrils is key to that restriction.
The “Energy” Organ
The lungs are the primary source of your energy level. They extract oxygen from the air we breathe primarily on the exhale. About 5% more of the oxygen in the air is extracted into our lungs when we exhale through the nostrils as well (air has been measure to enter ~21% and leave ~12% while breathing through the nose | ~21% and leaves at 16% through the mouth).
“When you exercise, carbon dioxide levels increase significantly which alert the chemoreceptors, which subsequently notify the brain’s respiratory center to increase the speed and depth of breathing. This elevated respiration rids the body of excess carbon dioxide and supplies the body with more oxygen, which are needed during aerobic exercise.” (Sarah Novotny and Len Kravitz, Ph.D, UNM, “The Science of Breathing”)
Nose Breathing and the Diaphragm
Because the nostrils are smaller then the mouth, air exhaled through the nose creates back flow of oxygen during the exhale. It slows the air escape so the lungs have more time to extract oxygen from them. They also increase the humidity of the air that travels into the lungs and Similar to closing the end of a teapot, breathing this way creates pressure in the diaphram and allows for a deeper exhale. A more complete exhale activates accessory breathing muscles to the fullest capacity which includes all of the abdominal muscles. All of this occurs muscularly while the sustained, increased oxygen level affect the muscles and nervous system regenerating it and allow the yogi to continue practicing. The key is slowing down the pacing so that the body can sustain its oxygen level.
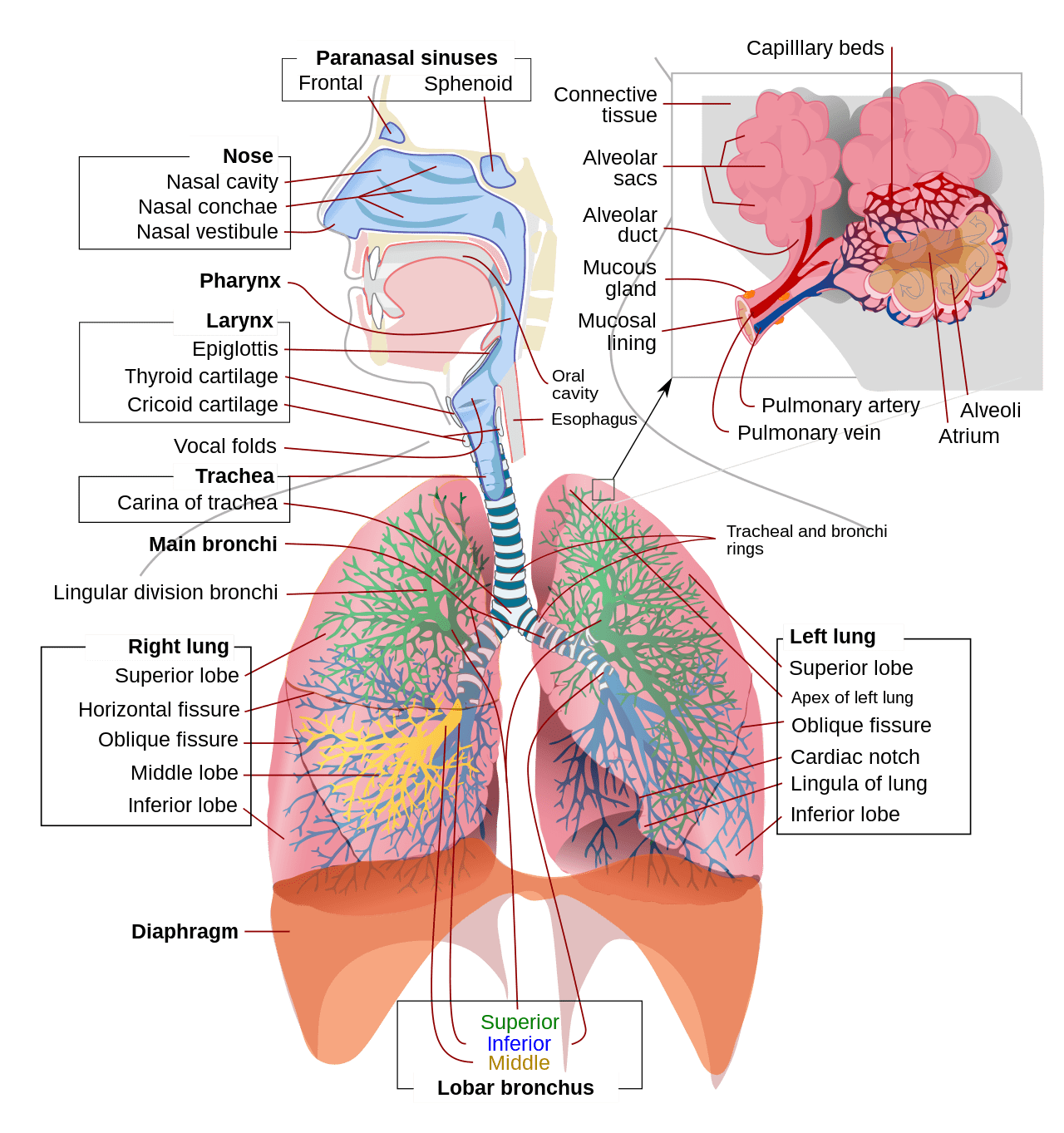
Let’s look at the different parts of the anatomy involved with breathing.
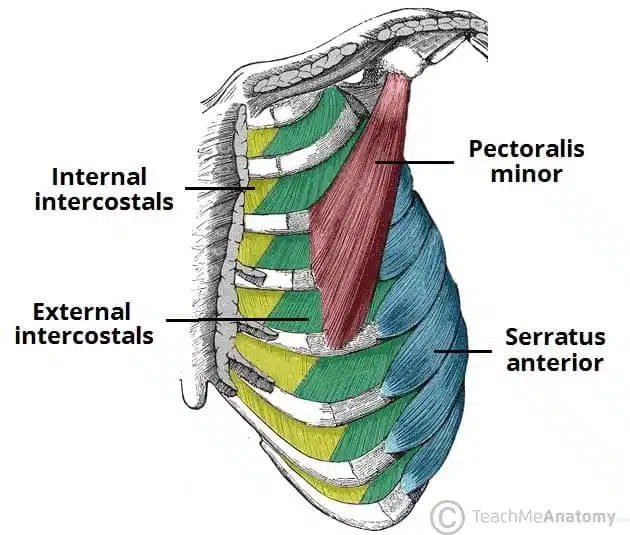
Muscles involved with Breathing
- Sternocleidomastoid
- Scalenes (neck)
- Trapezius
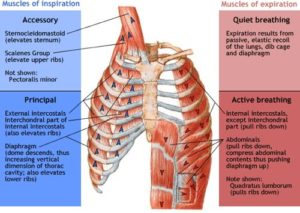
- Latissimus Dorsi (upper back)
- Pectoralis
- Diaphragm – primary breathing muscle
- Rectus
- Internal Obliques
- External Obliques
- Transverse Abdominus
- Serratus Muscles (ribs)
- Illiocostalis
- QL (lower back)
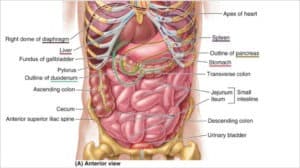
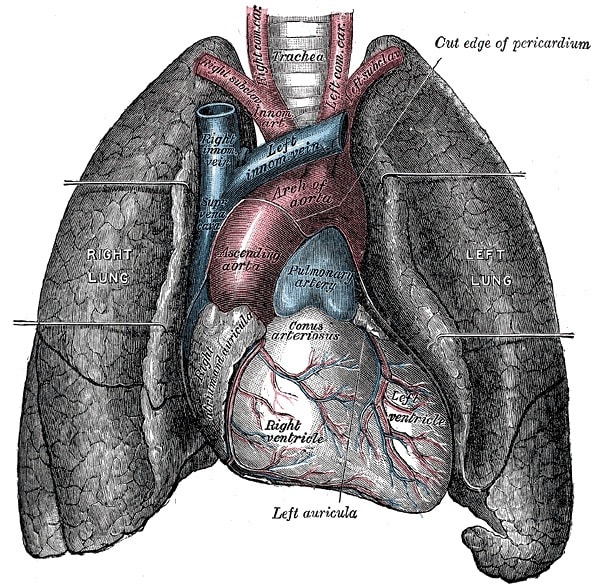
The bottom of the diaphragm is extremely important as it separates the upper portion of the torso from the lower and assists in the ventilation process. This is key to understanding why full capacity respiration is so important to the human body. Most of the organs lie within the Thorax, or chest cavity, so the lungs have a very complex and interesting relationship to the rest of the organs, especially the organs of the digestive tract.
How your Lungs Affect your Organ Anatomy
Because the nostrils are smaller than the mouth, air exhaled through the nose creates a back flow of air (and oxygen) into the lungs. And because we exhale more slowly through the nose than we do though the mouth, the lungs have more time to extract oxygen from the air we’ve already taken in. This affects the vital nervous system connections to your lungs and heart. Not breathing well through your nose can alter your heart rate and blood pressure. It can also increase the intensity and frequency of the human stress response. Many researchers have said that mouth breathing can also be misdiagnosed as ADHD. This is why yoga can be extremely important and useful for children and to alleviate the negative aspects of stress response (cortisol release).
That about does it for the known effects of respiration through the nose, although I’m sure the benefits to the organs, specifically the digestive tract are understated. Share what you know below!
References:
Nose Breathing & the Lungs Read More »